The sport of golf requires a harmonious blend of physical and mental skills. Golfers striving for improvement consistently seek innovative approaches to enhance their performance. Scientific principles offer a systematic and evidence-based framework to optimize training methodologies and enhance outcomes. This article delves into the multifaceted scientific aspects of golf training, examining the interplay of biomechanics, physiology, psychology, and technology.
Understanding Biomechanics and Swing Mechanics
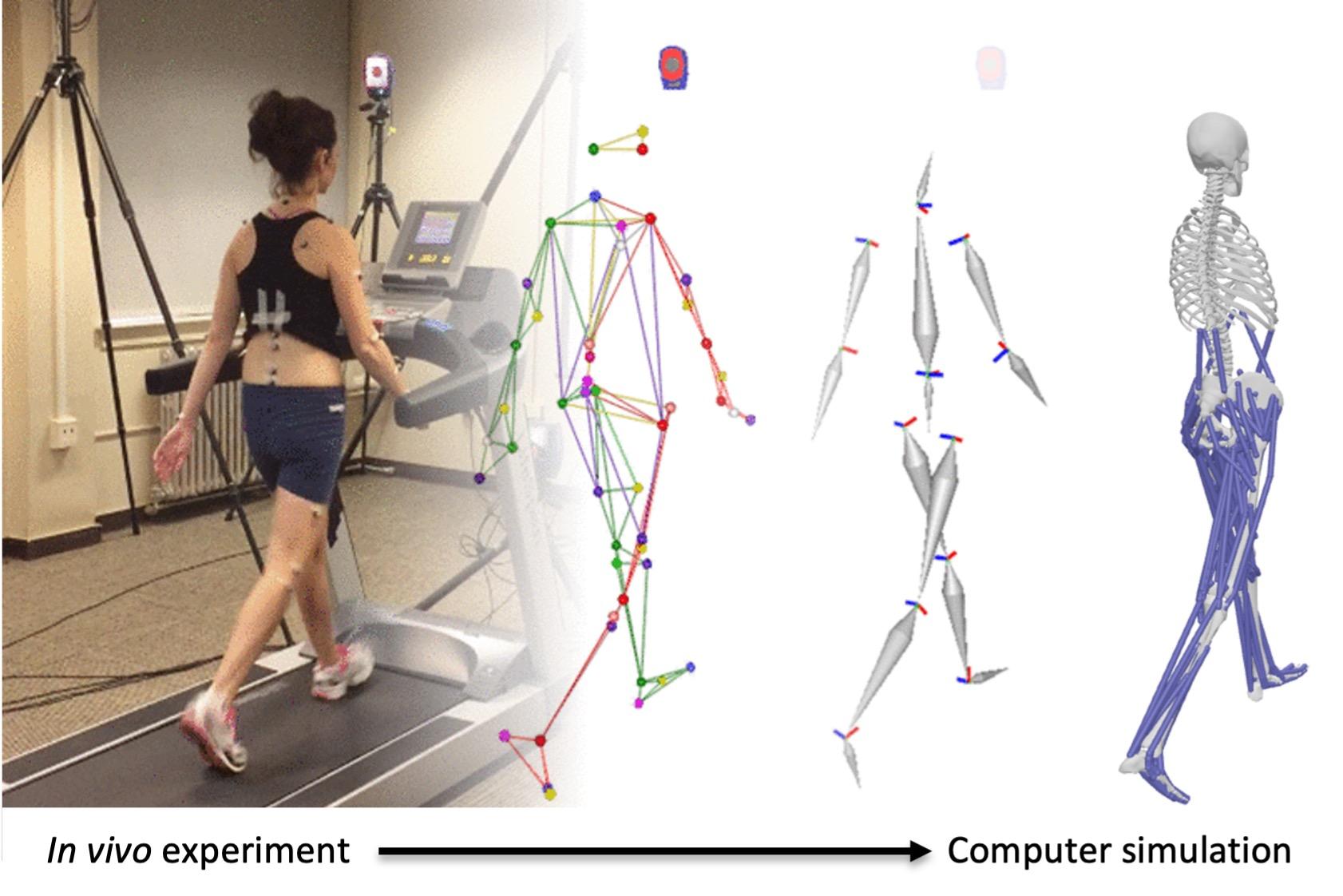
Understanding biomechanics is crucial for optimizing golf performance. Biomechanics analyzes the body’s movement and forces during the golf swing, providing insights into efficient and consistent techniques. By examining factors such as joint angles, muscle activation, and ground reaction forces, coaches and players can identify areas for improvement and reduce the risk of injury.
Swing mechanics, on the other hand, focuses on the sequence and timing of body movements in relation to the club and ball. Understanding the proper sequencing of the backswing, downswing, and follow-through is essential for maximizing ball velocity and accuracy. The swing plane, tempo, and path are all key components of swing mechanics that must be aligned to produce a powerful and consistent shot.
By analyzing both biomechanics and swing mechanics, golfers can develop a comprehensive training plan that addresses both the physical and technical aspects of the game. This integrated approach improves athleticism, reduces the risk of injury, and enhances swing consistency, ultimately leading to better scores and a more enjoyable golf experience.
Enhancing Muscle Activation and Physical Training
Properly activating muscles is crucial for efficient golf swings and overall physical training. Targeted exercises and training techniques can optimize muscle recruitment and enhance performance.
Eccentric Training: Emphasizing the eccentric (lengthening) phase of muscle contractions promotes greater muscle fiber activation and muscle damage, leading to increased strength and power. Exercises like controlled lowering of weights or negative reps in bodyweight drills can effectively enhance eccentric loading.
Neuromuscular Priming: Specific exercises and drills can activate the appropriate muscle groups and prime the nervous system for improved coordination and performance. For instance, banded external rotations for shoulders or hip thrusts with glute bridges can effectively target and prime the respective muscle groups for golf-specific movements. This activation enhances muscle coordination, power, and overall swing efficiency.
Optimize Practice Techniques and Skill Acquisition
- Incorporate Deliberate Practice: Structure your practice sessions to focus on targeted improvement, breaking down complex skills into smaller components. Emphasize consistency, intensity, and repetition with specific goals.
- Utilize Feedback and Analysis Tools: Leverage technological advancements such as video analysis, launch monitors, and performance tracking apps. Analyze data to identify areas for improvement, correct form, and monitor progress.
- Maximize Concentration and Focus: Create a conducive practice environment that minimizes distractions and enhances concentration. Engage in deep practice, where attention is fully dedicated to mastering the skill, fostering mindfulness and improving neural pathways.
Example Table: Practice Optimization Techniques
| Technique | Description | Benefits |
|—|—|—|
| Block Practice | Dividing practice into focused blocks for specific skills | Enhanced focus and skill isolation |
| Random Practice | Varying practice order among different skills | Promotes adaptability and decision-making |
| Extended Practice | Practicing beyond the point of initial skill mastery | Refines technique, increases consistency |
The Role of Cognitive Factors in Golf Training
Cognitive factors play a critical role in golf training, influencing both skill acquisition and performance. Mental imagery, for instance, allows golfers to vividly visualize successful shots, strengthening neural pathways associated with proper technique and enhancing confidence. Cognitive strategies, such as positive self-talk and attentional control, help golfers regulate their emotions and focus their concentration, particularly under pressure.
Furthermore, cognitive understanding of the game improves decision-making and shot selection. By comprehending the physics of ball flight and course management, golfers can make informed choices on club and swing type, optimizing their performance on every hole. This understanding also aids in troubleshooting, as golfers can analyze their shots and identify areas for improvement.
To promote cognitive development in golf training, coaches can incorporate several strategies. Video analysis allows golfers to observe their swings objectively and identify technical flaws or areas for improvement. Simulations provide a safe environment to practice cognitive skills, such as shot selection and course management, without the pressure of actual gameplay. Mindfulness techniques can enhance focus, concentration, and emotional regulation, translating into improved performance on the course.
Technology and Analytics for Performance Improvement
By leveraging various technologies and analytical tools, golf training has evolved into a data-driven field that enhances athlete development and performance. Trackers and sensors monitor key metrics such as clubhead speed, ball trajectory, and swing plane, providing valuable insights into each shot. High-speed cameras capture swing sequences, enabling coaches to identify and correct technical flaws. Analytics platforms process this data, generating benchmarks and predictions that personalize training plans and track progress.
Table: Key Metrics Tracked in Golf Training
| Metric | Description |
|—|—|
| Clubhead Speed | Velocity of the golf club’s head at impact |
| Ball Trajectory | Path and angle of the ball’s flight |
| Swing Plane | Imaginary line created by the golf club’s motion |
| Impact Angle | Angle at which the club strikes the ball |
| Club Path | Trajectory of the club’s travel toward impact |
Integrating advanced analytics into golf training has optimized performance outcomes. By analyzing data trends and patterns, coaches can identify specific areas for improvement. Machine learning algorithms create personalized practice simulations that target individual needs, maximizing the effectiveness of training sessions. Remote monitoring and virtual reality technologies connect players with off-site coaches, extending the reach and accessibility of professional guidance.
Conclusion
the science of golf training represents a multifaceted field that encompasses physiological, biomechanical, psychological, and technological aspects. By leveraging this scientific knowledge, golfers can enhance their performance metrics such as distance, accuracy, and consistency. Tailored training programs that address individual needs, coupled with cutting-edgetechnologies like motion capture and biofeedback systems, empower golfers to optimize their technique, prevent injuries, and maximize their on-course potential. As golf training continues to evolve, the integration of evidence-based practices and scientific principles will remain paramount for unlocking the full potential of the game.