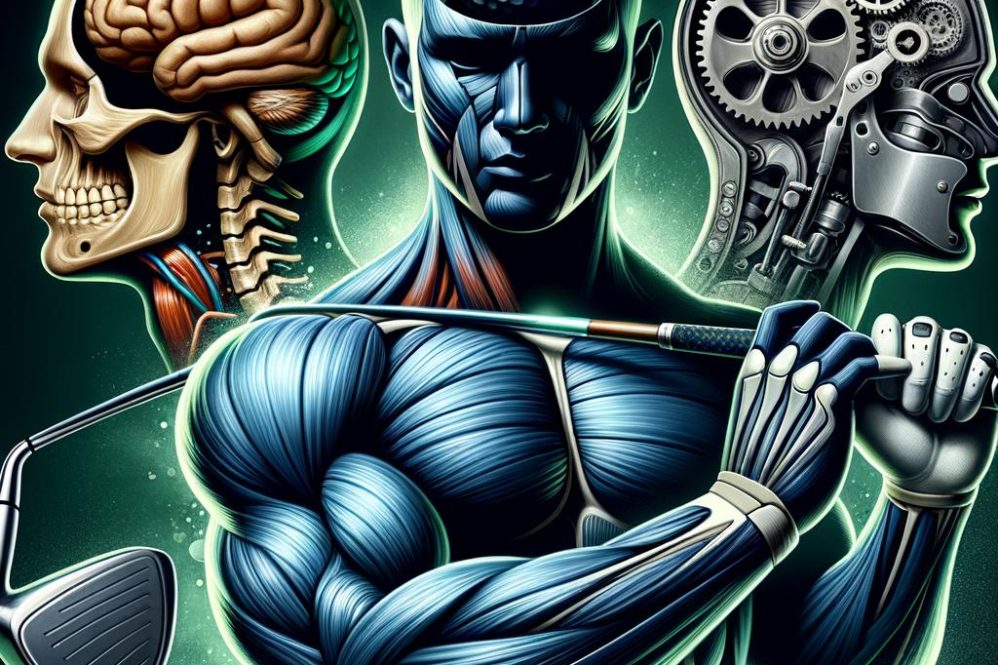
The emergence of “legend” status in sport is not reducible to raw totals or records alone; it also reflects cultural impact, long-term dominance, and the stories that coalesce around particular competitors. Contemporary definitions of “legendary” emphasize celebrated recognition, recurrent retelling, and distinction for unusual qualities. Placing elite golfers inside this conceptual frame requires both careful description-documenting the visible achievements and stylistic hallmarks that set iconic players apart-and analytic explanation of the systems and practices that produce and preserve high-level performance.
This feature approaches legendary golfers from a multidisciplinary standpoint, weaving together findings from sport psychology, biomechanics, performance analytics, and equipment science. It highlights psychological factors-resilience,attentional control,and competitive judgment-that allow players to deliver under pressure; the physical and motor-control foundations-strength,mobility,balance,and refined coordination-that permit repeatable technique; and strategic competencies-course architecture reading,shot-choice optimization,and risk management-that extend a player’s scoring advantage. Modern measurement and technology are given equal attention: data capture and analytics both illuminate key performance drivers and enable focused interventions,from swing-tuning to bespoke club fitting.
Bringing empirical evidence and conceptual models together, this review seeks to reveal the recurring features and causal pathways that separate genuinely legendary performers from their peers, draw out consequences for coaching and talent systems, and propose directions for future inquiry. The aim is to move past reverential accounts toward a methodical, evidence-based understanding of why some golfers rise above excellence to enduring legendary status.
Mindset and Mental Skills: Building Resilience,Focus,and Transferable Training Methods
Top-level golfers display a cluster of mental capabilities that sustain reliable performance across events and conditions. Grounded in contemporary psychological science, these athletes combine accurate threat appraisal, flexible coping tactics, and rapid emotional recovery to maintain consistency when stakes fluctuate. Research and applied practice show that resilience is not solely an innate trait but can be cultivated through graduated exposure to challenge,structured reflection,and progressive goal-setting; these processes bolster confidence and limit cascading performance collapses after mistakes.
Attention control is the mechanism that converts resilient mindset into executed shots. At the highest tiers, players move fluidly between an outward focus (target, environmental cues) and inward monitoring (swing tempo, breathing) depending on task demands, preserving working-memory capacity for key decisions while letting learned motor patterns operate automatically. Effective drills to strengthen this capability include:
- Fixed Pre-shot Rituals – standardized routines that reduce variability in arousal and attention when pressure rises.
- Short Mindfulness Breaks – brief breath-work or anchor cues to quiet distracting thoughts before execution.
- Simulated-Pressure Practices – practice tasks wiht scored consequences or audience simulation to desensitize stress reactions.
- Concurrent Load Drills - adding cognitive tasks during repetition to enhance automaticity under dual demands.
High-transfer training embeds psychological work within technical and physical sessions rather than treating it as an add-on. The compact chart below pairs core mental capacities with representative practice methods and the competitive outcomes coaches typically seek.Such schemata enable more precise allocation of practice time and objective tracking of how mental training affects shot-level performance.
| Mental Skill | Training Modality | Intended Competitive Benefit |
|---|---|---|
| Resilience | Incremental pressure exposures | Quicker rebound after errors |
| Attentional Control | Consistent pre-shot sequencing | Lower shot-to-shot variability |
| Emotion Regulation | Breath and biofeedback routines | Controlled arousal before shots |
To operationalize these ideas, adopt a cyclical, evidence-informed process that blends subjective reporting with objective indicators (validated questionnaires, heart-rate variability metrics). Key steps are: **profile** the player’s psychological baseline, **design** targeted interventions, **monitor** short-term response with brief quantitative measures, and **iterate** across training blocks. When mental-skills programming is periodized alongside technical and physical development, it more reliably produces the consistent competitive behaviors associated with historic performers.
Movement, Power, and Mobility: Biomechanical Principles and Conditioning for Repeatable swing Performance
Modern studies of elite swings frame performance through biomechanical principles-the analysis of motion and force in human movement as applied to golf. From this viewpoint, dependable ball-striking arises from the coordination of three interdependent domains: motor control, musculoskeletal capacity, and tissue pliability. Training thus targets not onyl isolated gains in strength or flexibility but the timed coordination of those qualities so club-head speed,launch conditions,and impact consistency become predictable outputs.
Neuromuscular control is the conduit by which physical ability becomes technical precision.elite players show highly consistent intersegmental timing, deliberate tempo modulation, and advanced proprioceptive sensitivity that minimize harmful variance at impact.Training priorities include:
- Sequencing drills – exercises that reinforce the correct proximal-to-distal activation order (pelvis → torso → arms → club).
- Sensorimotor training - balance, perturbation, and closed-chain tasks that enhance feedback and stability.
- Exposure to variability – constraint-based practice that preserves robustness across changing lies and conditions.
These capacities can be quantified on-course and in labs (motion capture, force plates), allowing interventions to be tailored to objective motor-control deficits.
strength and power must be interpreted through the lens of golf’s rotational and asymmetric movement demands; bilateral measures like a back squat 1RM are informative but incomplete. The table below links major anatomical contributors to practical conditioning targets and their functional role in the swing:
| Muscle Group | Representative Exercises | Functional Role |
|---|---|---|
| Core (obliques, transverse abdominis) | Anti‑rotation chops, Pallof press | Control and transfer of rotational torque |
| Hips & glutes | Single‑leg deadlift, lateral band walks | Ground-force generation and sequencing |
| Upper back & shoulders | Face pulls, thoracic rotation drills | Maintain spine posture and club delivery path |
Mobility is best judged by functional availability of range at speed and under load rather than static degrees of motion. Conditioning recommendations grounded in biomechanics include:
- Dynamic warm-ups that mirror swing positions and velocities.
- Progression to sport-specific power – moving from general strength into rotational power and integrated drills across mesocycles.
- Emphasis on controlled eccentrics to manage deceleration and reduce injury risk.
- Field metrics (rotational power tests,single-leg balance) to quantify adaptation and guide adjustments.
When packaged in individualized, periodized programs these principles optimize neuromuscular and mechanical readiness for consistent, high-quality swing performance while reducing injury risk and supporting longevity.
Shot Skill Development and Practice Architecture: Coaching Methods Backed by Motor learning
technical shot-making at the elite level should be treated as a set of interconnected sensorimotor skills and decision heuristics rather than isolated mechanical cues. This perspective reconciles classical mechanics-focused instruction with modern motor-learning theory: grip, stance, swing plane, and impact dynamics are functional instruments within a performer-habitat system organized to achieve scoring objectives.
Evidence-based coaching addresses both movement form and data processing. High-quality practice design combines motor-learning principles-deliberate practice, well-timed augmented feedback, and structured variability-with biofeedback and analytics. Core interventions include:
- Task breakdown (use constraints to isolate and simplify mechanics)
- Representative training (preserve perception-action links found in competition)
- Planned feedback (bandwidth or faded schedules to avoid dependency)
- Contextual variability (vary environmental and task conditions to boost transfer)
Practices should intentionally manipulate constraints to cultivate adaptable technique. The table below offers concise session prescriptions aligned with coaching goals; iterate these across microcycles and evaluate for retention and transfer rather than only immediate enhancement.
| Goal | Intervention | Expected Result |
|---|---|---|
| reliable ball-striking | Impact drills with video and sensor feedback | Improved clubface consistency |
| Performance under pressure | Variable practice under time or scoring constraints | Better transfer to tournament settings |
| Control of shot-shape | Constraint-led shaping tasks with target-focused feedback | Versatile perceptual-motor solutions |
Progress should be benchmarked with functional metrics-dispersion, carry distance consistency, and impact-location maps-and evaluated with retention and transfer tests rather than ephemeral accuracy gains. A mixed-methods assessment model-quantitative analytics plus qualitative movement appraisal-helps detect developing technical faults. Integrating a clear operational definition of “technical” with empirically validated practice design produces coaching interventions that are theoretically sound and practically effective for elite shot production.
Strategy, Course Management, and Decision Science: Practical Rules Informed by Analytics
Strategic excellence at the highest level treats shot selection as a decision problem under uncertainty. Using expected-value thinking and variance-management metrics, players and coaches can convert intuition into policies that aim to minimize total strokes across a round rather than seeking immediate, isolated advantages. Tools such as decision trees and Markov models help map course states (fairway, rough, hazard, green) and project outcome distributions for option plays, enabling principled trade-offs between safer, lower-variance options and riskier, higher-upside shots.
Tactical guidance flows directly from this analytic stance. A short set of priority heuristics simplifies in-play choices:
- maximize playability: select lies and angles that reduce the probability of catastrophic holes.
- Favor recoverability: aim for landing zones that leave multiple recovery routes rather than merely minimizing distance to the pin.
- Account for conditions: factor wind, turf firmness, and flag placement into probabilistic club decisions.
These simple rules reconcile complex models with the mental bandwidth available during competition.
Equipment and technology shifts alter the underlying distributions of shot outcomes and thus must be integrated into strategic models. innovations in putter design, shaft materials, and ball aerodynamics change launch windows and dispersion patterns, shifting computed risk-reward balances. The illustrative table below shows how a decision framing might differ by situational parameters (probabilities are schematic):
| Choice | Success Probability | Estimated Strokes Saved |
|---|---|---|
| Conservative (lay-up) | 0.90 | 0.15 |
| Aggressive (carry hazard) | 0.55 | 0.40 |
Performance under pressure demands the marriage of analytics with behavioral tactics: employ pre-commitment rules (e.g., a club-choice policy), structured caddie consultation routines, and strict time management to limit decision noise. In match play, opponent modeling and simple game-theoretic thinking-using mixed strategies and on-the-fly adjustments-can open tactical edges. Practically, teams should create a pre-round game plan, carry a concise decision checklist during play, and update model parameters after rounds to close the learning loop and improve strategy over time.
Sensors, Models, and fitting: How Analytics Shape Equipment Choices and Ongoing Monitoring
Modern performance optimization treats athlete and equipment as an integrated measurement problem: sensor fusion captures fine-grained data on ball flight, club kinematics, and human biomechanics, which are then standardized into metrics for comparison and inference. Raw streams from launch monitors, high-speed cameras, IMUs, and force plates require cleaning, synchronization, and normalization so that changes to club-head mass, shaft stiffness, loft/lie, or ball model can be evaluated against stable baselines. Proper instrumentation enables stronger causal claims-testing how a specific hardware tweak shifts launch window,spin,or dispersion under controlled conditions.
Analytics pipelines convert measurement into prescriptions through layered modeling: descriptive summaries, predictive forecasts for candidate setups, and prescriptive optimization that recommends parameter values suited to a chosen objective (distance vs. accuracy tradeoffs, for example). Commonly integrated data sources include:
- Launch monitors (ball speed, spin, launch angle)
- Optical tracking and high-speed video (club path, face angle)
- Wearables and IMUs (tempo, angular velocity)
- Force platforms (weight transfer and ground-reaction profiles)
Moving from analytics to equipment decisions combines algorithmic suggestions with empirical A/B testing.Well-designed comparative trials let fitters and coaches validate model-recommended changes (shaft flex, loft tweaks, grip adjustments) against the golfer’s objective function. The decision matrix below summarizes typical measured issues and corresponding adjustments:
| Measured Issue | Typical Adjustment |
|---|---|
| Excessive backspin | Reduce loft / test lower-spin ball models |
| Low launch | increase loft / fit a higher-launch shaft |
| Wide dispersion | Adjust lie/shaft, refine grip or stance |
Ongoing monitoring draws on longitudinal analytics and anomaly detection to hold performance steady and spot decline from fatigue, injury, or equipment degradation. Time-series models flag meaningful shifts in key indicators and trigger refitting or training changes when drift passes tolerance limits. Operational best practices include consistent measurement protocols, versioned data pipelines, periodic re-validation of model outputs, and governance that protects athlete privacy and ensures informed consent. Together these elements create a data-informed ecosystem where equipment selection and performance monitoring are continuously optimized to support elite output.
Recovery, Fueling, and Injury Prevention: Practical Protocols to Sustain Competitive Readiness
Elite golfers benefit from a structured recovery system that is both evidence-based and scalable. Core pillars are optimized sleep and circadian alignment,deliberate periodization of on-course and gym workloads,and multimodal recovery tools-active recovery,neuromuscular facilitation,and temperature-based modalities. Social supports and accessible mental-health resources-modeled on peer-supported recovery frameworks-can also reinforce resilience and provide low-stigma avenues for care.
Nutrition should be aligned to golf’s intermittent, precision-focused demands and individualized metabolic profiles. Key, practical components include:
- energy matching: align caloric intake with daily training and competition load to sustain neuromuscular capacity and hormonal health.
- Protein distribution: regular servings of high-quality protein across the day to support repair and adaptation.
- Carbohydrate timing: targeted carbohydrate intake to fuel repeated-power efforts and recovery between rounds.
- Micronutrients & anti-inflammatory choices: maintain vitamin D status, include omega‑3 sources, and favor polyphenol-rich foods to support bone, immune, and soft-tissue health.
Preventive medicine and biomechanical screening reduce downtime.Routine movement screens (thoracic rotation, hip rotational strength, scapular control), eccentric and rotational strength work, and load-management plans lower overuse risk and help preserve swing mechanics. The table summarizes typical interventions and their evidence profile in applied golf contexts.
| Intervention | main Mechanism | Evidence Level |
|---|---|---|
| Rotational strength training | Improves torque transfer and swing stability | Moderate-High |
| Thoracic mobility drills | Restores range needed for efficient kinematics | Moderate |
| eccentric hamstring loading | Reduces soft-tissue strain in deceleration | Moderate |
| Sleep and circadian optimization | Supports cognitive and motor consolidation | High |
Putting these protocols into practice requires interdisciplinary coordination among coaches, sports scientists, dietitians, physiotherapists, and mental-health clinicians. Objective monitoring-wearables for load and sleep, nutrition tracking, and standardized pain/function scales-enables adaptive programming. When specialized behavioral health or addiction treatment is required, referral pathways to regional services can maintain continuity of care without derailing athletic development. In sum, individualized, evidence-based recovery and prevention frameworks preserve long careers and allow high-level skills to be expressed consistently during competition.
Developing Future Legends: pathways,Measurement,and Policy for Long-Term Athlete Growth
Deliberate developmental pathways are essential for moving talented juniors toward elite and perhaps legendary careers. A staged approach-broad early sampling across multiple sports, cautious specialization later, and progressively more refined competitive exposure-reduces burnout and supports transferable skill acquisition. Critical infrastructure includes mentorship systems, sequenced skill curricula, and alignment between grassroots clubs, regional centers, and national programs. Strong pathways balance structured deliberate practice with play-based learning and provide stage-appropriate supports (nutrition, sports psychology, movement screening).
Measurement strategies for talent work should be multidimensional, longitudinal, and developmentally sensitive. Beyond raw scoring,systems should integrate indicators across physical,technical,cognitive,and psychosocial domains. Typical measurement domains include:
- Physical: mobility, power markers, endurance, injury-risk profiling
- Technical: shot dispersion patterns, tempo stability, short-game efficiency
- Cognitive/psychological: decision speed, stress tolerance, focus under duress
| Stage | Representative Measure | Assessment Cadence |
|---|---|---|
| Foundation | Movement competency index | 6-12 months |
| Specialization | Shot-dispersion tendencies (yards/meters) | 3-6 months |
| Mastery | Tournament performance variability | Event-based |
Policy recommendations should align incentives, professionalize coach education, and protect athlete welfare to build fair and sustainable talent pipelines.Specific steps for governing bodies and funders include:
- Fund coach development focusing on LTAD principles and data-literate practice design
- Create financing models that reward long-term development over short-term competitive success
- Require standardized monitoring frameworks with clear data-governance rules to protect privacy and enable multicenter research
Putting policies into action demands collaboration across sport science institutes,clubs,universities,and federations. Pilot programs should use mixed-method evaluations-pairing longitudinal quantitative tracking with qualitative process reviews-to iteratively refine pathways. Prioritize scalable tools (portable movement screens, standardized shot analytics, shared data platforms) and open research-practice feedback to accelerate adoption while safeguarding athlete welfare and expanding access across socioeconomic groups.
Q&A
Prefatory note
“Legendary” describes enduring fame and exceptional achievement (see common dictionary usages). In golf, a “legendary golfer” is an athlete whose prolonged competitive success, lasting influence on the game, and demonstrable superiority across psychomotor, cognitive, and strategic dimensions place them well above standard professional norms.
Q&A: Defining and Studying Legendary Golf Performance
1. Q: How can researchers define a “legendary golfer” for empirical analysis?
A: Construct a composite measure that blends objective performance indicators (major titles, career victories, scoring metrics, strokes-gained profiles), measures of longevity and consistency (years at top percentile, seasonal stability), and qualitative impact markers (peer recognition, influence on equipment or technique, hall-of-fame induction). Weighting these components allows cross-player and cross-era comparisons and supports sensitivity testing of alternative definitions.
2. Q: What psychological features separate legendary golfers from other pros?
A: Distinguishing mental characteristics include well-developed stress inoculation, superior attentional control, disciplined pre-shot routines, adaptive goal setting, and robust recovery from setbacks.These traits combine with decision-calibration abilities and measured risk tolerance to produce consistently effective choices under uncertainty.
3. Q: How do strategy and course management contribute to elite outcomes?
A: Legendary players excel at probabilistic course modeling-folding wind, lie, hazards, and opponent scoring into shot selection. They favor strategies that optimize expected tournament returns across rounds, display refined club selection in uncertain conditions, and dynamically update game plans as the scoring context changes.The capacity to toggle between conservative and aggressive strategies is a hallmark.
4. Q: Which physical characteristics best predict elite golf success?
A: Predictive attributes include efficient rotational power and kinetic-chain transfer, refined fine-motor control for short-game subtleties, dynamic flexibility (torso, hips, shoulders), and coordinated sequencing. Aerobic and muscular endurance help maintain consistency across multiple rounds and long seasons.
5. Q: What does biomechanics reveal about exceptional shot-making?
A: Biomechanical study shows legendary shots emerge from optimal proximal-to-distal sequencing, minimized nonessential segmental motion, and a stable base-factors that yield reproducible impact conditions (club‑head speed, face angle, and path).Small temporal or angular deviations can produce large outcome changes, which biomechanics helps quantify and correct.6. Q: How do practice habits differ between legendary golfers and their peers?
A: Differences are usually qualitative: top legends emphasize high-fidelity deliberate practice that mirrors competition,integrate physical and technical training,periodize conditioning,and use evidence-based recovery.They routinely use pressure simulations and work with multidisciplinary teams (biomechanists,sports psychologists,data analysts) for cohesive planning.
7. Q: In what ways has advanced analytics reshaped elite preparation?
A: Shot-level datasets, ball-flight tracking, and strokes-gained models deliver granular diagnostics that pinpoint strengths and weaknesses, shape course-specific plans, and prioritize practice areas by expected strokes saved. Analytics also guide individualized equipment and swing decisions by estimating scoring impact from technical changes.
8. Q: How much does equipment affect the gap between elite and legendary performance?
A: Equipment can raise performance ceilings-altering ball speed, spin, and dispersion-but it does not replace the cognitive and motor skills that define legendary status. The most influential players marry equipment to their biomechanical profile to extract marginal advantages that accumulate over a career.
9. Q: What methods are suitable for comparing players across different eras?
A: Cross-era work requires normalizing for equipment evolution, course length and setup, agronomy, and competitive depth. Techniques include benchmarking against contemporaneous field averages, computing z-scores, and simulation models that project player performance under alternative conditions; archival qualitative analysis supplements quantitative adjustments.
10. Q: How can clutch performance and pressure resilience be quantified?
A: Operationalize clutch behavior by contrasting expected outcomes from shot-level models with observed results in high-leverage contexts (final-round shots, playoffs, high-pressure putts). Time-series models controlling for opponent and course variables,together with in-event psychophysiological metrics (e.g., HRV), can triangulate the resilience construct.11. Q: What role do talent identification and early specialization play in producing legends?
A: Effective identification leverages multidimensional profiling-motor ability, perceptual-cognitive skill, learning adaptability, and psychological robustness. Early specialization offers benefits for focused deliberate practice but risks reduced adaptability; many successful pathways combine early sampling with later targeted specialization.
12. Q: Which injuries are most common for elite golfers and how are they mitigated?
A: Common problems include lumbar overload, elbow tendinopathies, and shoulder strains tied to repetitive rotational loading and asymmetry.Prevention and management involve targeted conditioning (core and hip stability), swing adjustments to decrease harmful loads, workload monitoring, and staged rest and rehab through a multidisciplinary team.13.Q: How do social and environmental factors affect elite development?
A: Quality coaching relationships, multidisciplinary support, a culture of iterative improvement, and stable financial backing materially influence career trajectories. Mentorship, peer learning, and environments that permit experimentation while enforcing standards support the rise of elite performers.
14. Q: What ethical and practical issues accompany increasing tech use in elite preparation?
A: Ethics centre on equitable access, data privacy, and the risk of overreliance on analytics at the expense of perceptual skill. Practically, technology must be validated and interpreted by trained coaches, with clear algorithms and clear governance to protect competitive integrity.
15. Q: Which research areas will most deepen our understanding of legendary performance?
A: High-value directions include longitudinal multimodal research linking kinematics, physiology, and psychosocial data to real outcomes; randomized interventions testing psychological or biomechanical protocols; machine-learning models that quantify scoring impacts of technical changes; and cross-cultural analyses of development systems. Translational work that produces scalable coaching tools will yield the greatest applied payoff.
16. Q: What should coaches and practitioners take away from this review?
A: Adopt multidisciplinary, evidence-based practices that blend mental skills training, biomechanical refinement, and strategic planning. Prioritize high-fidelity deliberate practice, bespoke equipment fitting, structured load management, and realistic competition simulations.Analytics must be interpreted within each athlete’s biopsychosocial context and directed toward interventions that demonstrably improve scoring.
17. Q: How can amateur players apply lessons from legendary golfers without elite resources?
A: Recreational players should focus on high-return fundamentals: consistent pre-shot routines, purposeful short-game practice, basic strength and mobility work, and conservative course management that plays to their strengths. Using publicly available shot maps, affordable training aids, and time-efficient deliberate practice can accelerate improvement without elite infrastructure.
References and sources for terminology
– Standard dictionary usages for “legendary” (common lexicons). (Contextual only; the performance literature summarized above is drawn from contemporary sport science, biomechanics, and applied analytics.)
This synthesis has described the multidimensional nature of golfers typically labeled “legendary.” beyond inherent talent or isolated technical skill, legendary performance is the product of sustained psychological robustness, precise motor abilities, strategic sophistication, and the bright request of analytic and equipment tools. Practically, the analysis underscores integrated development pathways that combine biomechanical and motor-control practice with systematic mental-skills training and decision frameworks.Coaches and performance teams should view data-driven fitting and analytics as complementary to-not replacements for-individualized coaching and on-field experience.Talent programs will benefit from metrics that capture adaptability, learning velocity, and situational judgment alongside traditional physiological and technical indicators.
Methodologically, future work should fill gaps with longitudinal, mixed-method designs linking biomechanical, cognitive, and psychosocial measures to competitive outcomes; randomized or controlled interventions that establish causal effects; and broader samples examining cultural and developmental diversity among elite performers.Data-privacy, equitable access, and ethical governance must accompany efforts to scale analytic innovations.
Understanding what makes a golfer “legendary” requires a multidisciplinary approach that integrates theory, measurement, and practice. By combining insights from sport science, psychology, and technology, practitioners and researchers can better create the conditions that foster exceptional, durable performance-advancing both scientific knowledge about expertise and the applied pursuit of excellence in golf.
Masters of the Game: Decoding the Elite Performance of Golfing Icons
What separates legendary golfers from the rest is not a single trait but a consistent blend of superior golf swing mechanics, mental resilience, strategic course management, adn smart use of technology. This article breaks down the core pillars of elite performance-mental, physical, technical and technological-and provides practical, research-aligned guidance you can apply to training, coaching, or competitive planning.
What “Elite Performance” Looks Like in Modern Golf
elite performance in golf is multidimensional. Top players score consistently under pressure, maintain superior ball-striking and short-game percentages, and leverage analytics to decision‑make. Key performance indicators commonly used by coaches and analysts include:
- Scoring average and relation to par
- Strokes Gained (Off-the-Tee, Approach, Around-the-Green, Putting)
- GIR (Greens in Regulation) and proximity to hole
- Driving distance and driving accuracy
- Scrambling and up-and-down percentages
- Performance under pressure (final-round scoring differential)
Mental Game: The Cognitive Edge of Legendary Golfers
Golf is often described as 90% mental.Legendary golfers cultivate mental skills that allow them to perform reliably in high-stress situations.
core psychological traits
- Resilience: rapid recovery from poor shots or holes
- Focus & attention control: maintaining present‑moment concentration
- Shot-level routines: pre-shot and post-shot rituals that re-center attention
- Emotional regulation: controlling arousal and anxiety during competition
Practical mental training drills
- Mindfulness + breathing: 3-5 minute pre-round mindfulness to reduce cognitive noise
- Visualization: rehearsing successful shots and outcomes in vivid sensory detail
- Pressure training: simulate score pressure in practice (e.g., counting up or betting formats)
- Chunking: break rounds into manageable segments (holes 1-3, 4-6, etc.) to limit rumination
Biomechanics & the Modern Golf Swing
elite golfers optimize a repeatable kinematic sequence and use ground reaction forces, body rotation, and efficient energy transfer to generate speed and accuracy.
Key biomechanical principles
- Kinematic sequence: pelvis → torso → arms → club for efficient power transfer
- Ground force utilization: pushing into the ground for added clubhead speed
- Separation (X-factor): controlled differential between hip and shoulder rotation
- Centering and balance: consistent ball-striking requires stable base and posture
Training recommendations
- Film swings regularly (high-speed camera) and review with a coach for key sequence errors
- use medicine ball rotational throws and resisted band work to improve separation
- Prioritize hip mobility, thoracic spine rotation, and ankle stability
- Perform speed-sessions with overspeed training (carefully and under supervision)
strategy & Course management: Thinking Like a Champion
Course management is where mental game and technical skill meet. Legendary golfers treat a course as a puzzle-decisions are guided by risk-reward analysis, statistical thinking, and situational awareness.
Decision-making framework
- Assess the hole geometry, wind, lie, and pin position.
- Estimate probabilities (e.g., likelihood of hitting green from current distance).
- Choose the option with the highest expected value given your strengths.
- Execute the selected play with a confident, rehearsed routine.
Practical strategic tips
- Play to your miss-know where your ball typically lands when you miss and use that to guide aiming points.
- Choose clubs with an eye on approach angles and recovery options (e.g., favor controlled mid-irons over low-percentage driver plays).
- Use front-versus-back pin strategy: when in doubt, aim for the fat part of the green.
Technology & Data Analytics: From Launch Monitors to Strokes Gained
Data and technology have transformed how elite players train. Devices including TrackMan, GCQuad, ShotLink data, and wearable sensors provide precise metrics that drive improvements.
Core technologies and their uses
- Launch monitors (TrackMan/GCQuad): ball speed, launch angle, spin, carry, clubhead speed
- ShotLink and Strokes Gained analytics: identify where strokes are won/lost relative to the field
- High-speed video & motion capture: diagnose sequence issues and timing
- Simulators and AI coaching platforms: structure practice sessions and create situational reps
How to integrate tech into practice
- Start with Strokes Gained to target weaknesses (e.g., putting vs approach play).
- Use launch monitor sessions to verify changes in clubhead speed and spin after technical adjustments.
- Periodically re-fit clubs based on consistent tracked metrics rather than feel alone.
Practice Design: From Purposeful Practice to On-Course application
Elite performance stems from deliberate, varied, and outcome-focused practice rather than mindless repetition.
Practice principles
- Deliberate practice: short, focused sessions with immediate feedback
- Contextual interference: mix shot types and conditions (random practice) to build adaptability
- Specificity: practice under conditions that replicate competition (e.g., pressure putts, uneven lies)
- Recovery & load management: schedule rest and active recovery to avoid overtraining
Weekly training sample (simple WordPress-styled table)
| Day | Focus | Key Drills |
|---|---|---|
| Monday | Mobility & Strength | Thoracic rotation, single-leg deadlift, core anti-rotation |
| Tuesday | Range – Ball Striking | Sequenced swing drills, 9-12 clubs, launch monitor feedback |
| Wednesday | Short Game | 50-100 reps: bunker, chips to varied targets |
| thursday | Putting | Distance control + 10 pressure putts from 3-6 ft |
| Friday | on-course Strategy | Play 9-18 holes focusing on course management |
| Saturday | Speed & Power | Short sprints, plyometrics, overspeed swings |
| Sunday | Recovery & Review | Active recovery, video review, mental prep for week |
Equipment & Club Fitting: Precision Tools for Performance
Legendary golfers rely on equipment optimized to their swing profiles. The right shaft, loft, head design, and ball choice support consistency and maximize strokes gained.
Fitting priorities
- Shaft flex and kick point matching speed and tempo
- Loft and lie adjustments for optimal launch and dispersion
- Club head selection for center-of-gravity and forgiveness needs
- Ball choice: match compression and spin characteristics to your swing
Case Studies: How Integrated Approaches Create Breakthroughs
Two short, illustrative examples (anonymized) of how combined mental, physical and technological interventions produce measurable gains.
Case study A – Driver distance & accuracy
- Baseline: adequate clubhead speed but inconsistent impact and low spin.
- Intervention: swing sequence correction via motion capture + strength programme for hip drive + launch monitor tuning for optimal loft.
- Outcome: 6-10 yards of carry gained on average and tighter dispersion (measured over 50 shots).
Case study B - Putting performance under pressure
- Baseline: excellent stroke mechanics but poor pressure conversion in competition.
- Intervention: pressure-simulated practice (replicated tournament holes), pre-putt breathing routine, and green-reading template.
- Outcome: improved 3-6 ft conversion rate and measurable drop in three-putts per round.
Benefits & practical Tips for Players and Coaches
- Benefit: Data-driven tweaks can quickly identify high-leverage improvements (e.g., improve approach shots to reduce scores).
- Tip: Use Strokes Gained to prioritize training-focus where you lose the most strokes.
- Tip: Develop a simple, repeatable pre-shot routine and practice it until it’s automatic.
- Tip: Keep a performance journal-track practice content, mental state, and outcomes to spot patterns.
Coach & Player Checklist: Roadmap to Elite Performance
- Baseline testing: mobility, strength, launch monitor metrics, putting stats
- Set 90-day targeted goals (distance, GIR, short-game conversion)
- Design weekly microcycles combining technical, physical, and mental work
- Incorporate regular technology checks (monthly launch monitor, quarterly fitting)
- Monitor recovery and adapt loads based on performance and fatigue
Additional Resources & Next Steps
Players aiming for elite performance should blend objective data (launch monitor, Strokes Gained) with subjective coaching, regular biomechanical assessment, and structured mental training. If you’d like, I can tailor this article to an academic audience with citations and study references, a magazine-friendly feature with profiles of iconic champions, or a coach-focused checklist with printable templates.
SEO keywords embedded naturally throughout this article: legendary golfers, elite performance, golf swing, mental resilience, course management, golf analytics, biomechanics, golf equipment, strokes Gained, driving distance, putting, short game, trackman, club fitting.








